Major Cities:
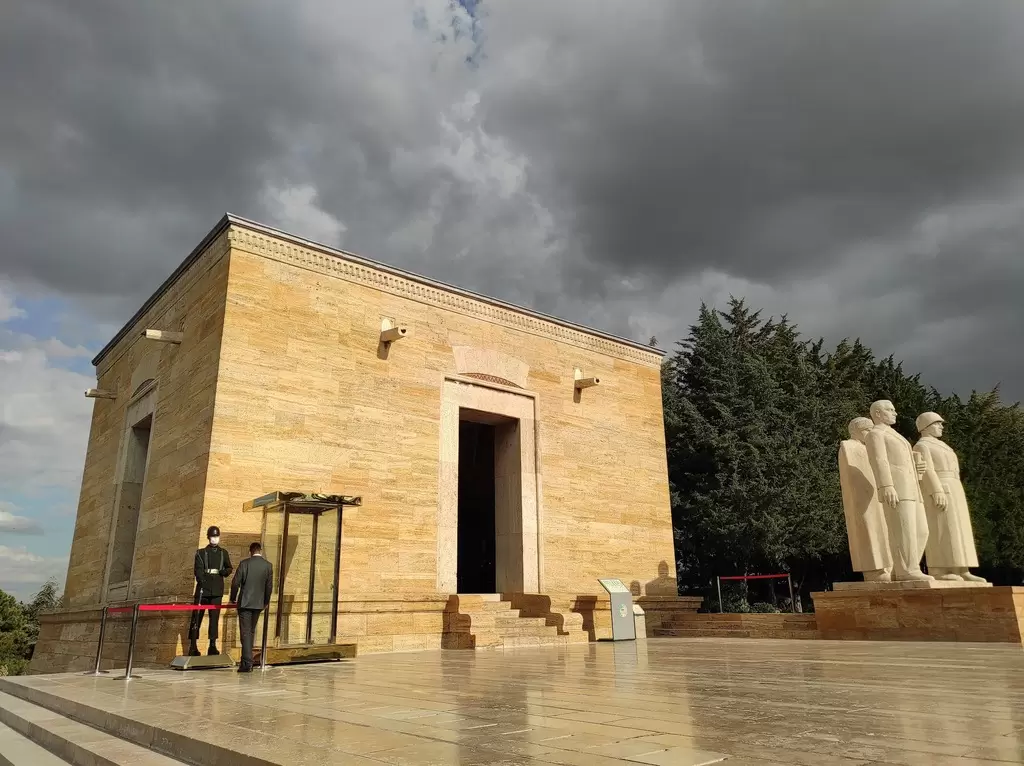
- Ankara: As the capital of Turkey, Ankara is the largest city in Central Anatolia and the second-largest in the country. Besides being the political center, Ankara is also a vibrant cultural hub, hosting museums, theaters, and art galleries. The city is known for its modern architecture, including the iconic Ataturk Mausoleum (Anıtkabir).
- Konya: Konya is one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in Turkey and holds great cultural significance as the center of the ancient Seljuk Empire. It is famous for its stunning architectural landmarks, such as the Mevlana Museum (dedicated to the poet Rumi), the Alaaddin Mosque, and the Karatay Medrese.
- Nevşehir: Located in the historical region of Cappadocia, Nevşehir is renowned for its unique rock formations, underground cities, and cave dwellings. The region's surreal landscapes and hot air balloon rides make it a popular tourist destination.
- Kayseri: Kayseri is a bustling industrial and commercial center in Central Anatolia. The city boasts a rich historical heritage, including the Seljuk-era Kayseri Castle and the Gevher Nesibe Museum, which was once a medical university.
- Aksaray: Aksaray is known for its historical sites, such as the ancient city of Nora and the Sultanhanı Caravanserai. The region is also recognized for its agricultural production, particularly in terms of grains and fruits.
- Eskişehir: Eskişehir is an important industrial and educational center. It is known for its vibrant cultural scene, featuring art festivals, museums, and the Porsuk River, which runs through the city.
Economy:
Central Anatolia has a diverse economy driven by various sectors. Agriculture plays a significant role, with the region being known for its production of wheat, barley, sugar beets, potatoes, and livestock. The region is also rich in mineral resources, such as coal and boron, which contribute to its mining industry. Furthermore, Central Anatolia is an important manufacturing and industrial hub, with sectors including textiles, automotive, machinery, ceramics, and defense.
Tourism:
Central Anatolia offers unique attractions and historical sites that draw tourists from around the world. Some of the notable destinations include:
- Cappadocia: Located primarily in Nevşehir and Kayseri provinces, Cappadocia is renowned for its otherworldly landscapes of cone-shaped rock formations and fairy chimneys. Visitors can explore underground cities, cave churches, and take hot air balloon rides to enjoy panoramic views.
- Hattusha: The ancient capital of the Hittite Empire, Hattusha is a UNESCO World Heritage site. It features well-preserved ruins, including city walls, temples, and the Lion Gate.
- Ankara Citadel: Situated in the heart of Ankara, the citadel is a historic fortress that offers panoramic views of the city. It houses ancient Roman, Byzantine, and Ottoman structures.
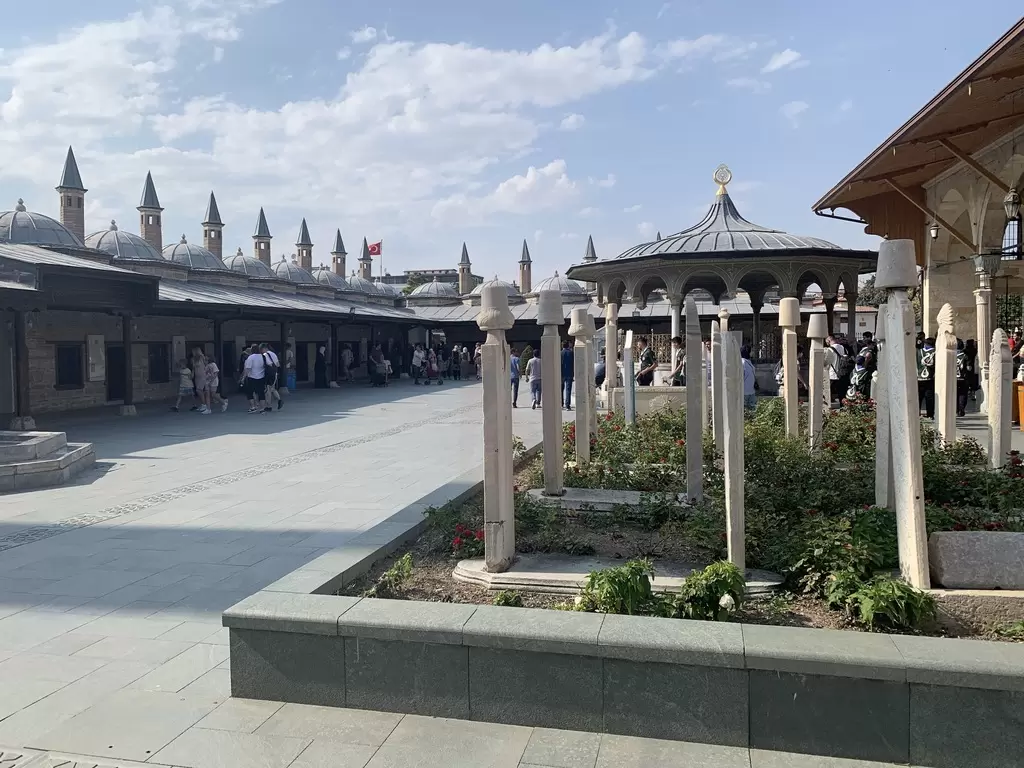
- Mevlana Museum: Located in Konya, the Mevlana Museum is dedicated to the renowned Sufi poet and philosopher, Rumi (Mevlana). It showcases his tomb, exhibits related to Sufi culture, and hosts the mesmerizing Whirling Dervishes performances.
Transportation:
Central Anatolia has a well-developed transportation infrastructure. It is connected to other regions of Turkey through highways, railways, and domestic airports. Ankara has an international airport, and there are regional airports in other major cities, facilitating both domestic and international travel.
Natural Features:
Central Anatolia is characterized by its vast plains, plateaus, and volcanic landscapes. The region is home to the Kızılırmak River, Turkey's longest river, and the Salt Lake (Tuz Gölü), one of the largest salt lakes in the world. The volcanic formations of Cappadocia and the Ihlara Valley, with its scenic beauty and rock-cut churches, are among the region's natural highlights.
Cultural Significance:
Central Anatolia boasts a rich historical and cultural heritage, influenced byvarious civilizations that have inhabited the region throughout history. It was an important center for ancient civilizations, including the Hittites, Phrygians, Persians, Romans, Byzantines, and Seljuks. The region's historical sites, museums, and traditional festivals showcase this diverse heritage.
The cuisine of Central Anatolia reflects its agricultural abundance and cultural diversity. Popular dishes include mantı (Turkish dumplings), etli ekmek (meat bread), Testi kebabı (a type of meat stew cooked in a clay pot), and various traditional pastries.
In summary, Central Anatolia encompasses a wide range of historical, cultural, and natural attractions. From the surreal landscapes of Cappadocia to the ancient ruins of Hattusha and the vibrant cities of Ankara and Konya, the region offers visitors a unique blend of history, natural beauty, and Turkish hospitality.


















