Major Cities:
The Southeast Anatolia region is home to several significant cities, including:
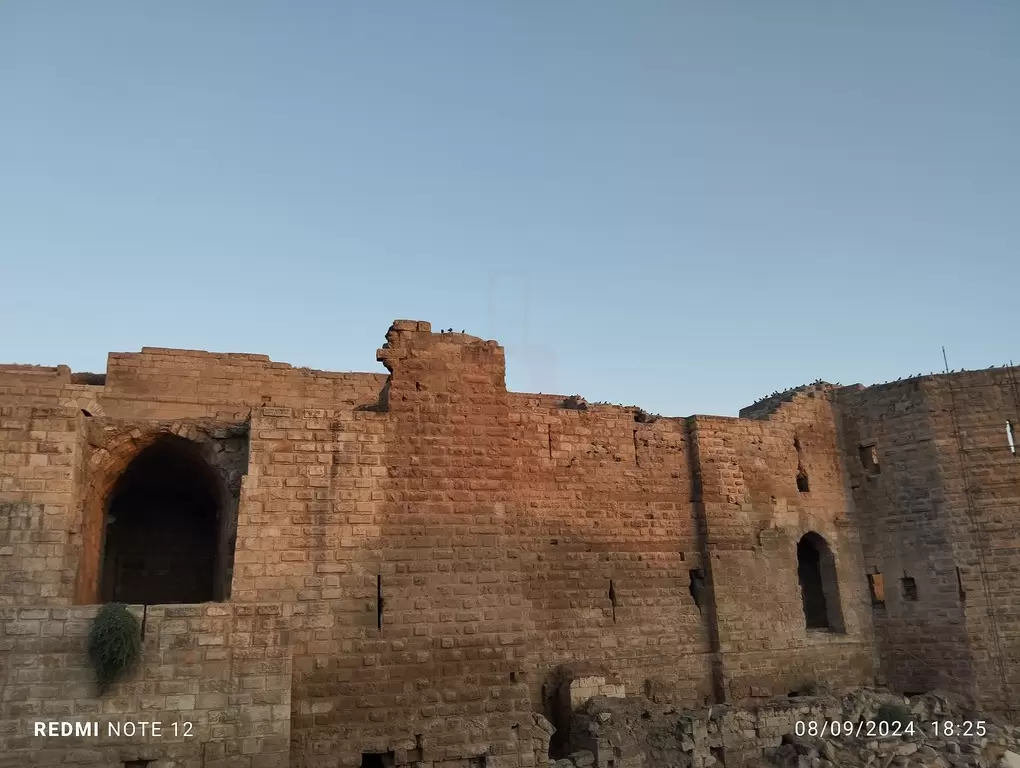
- Diyarbakır: Diyarbakır is the largest city in the region and serves as its cultural and economic center. It is renowned for its well-preserved city walls, which date back to Roman times. Diyarbakır is also known for its historic mosques, bazaars, and the ancient Hasankeyf, an archaeological site that was relocated due to the construction of the Ilısu Dam.
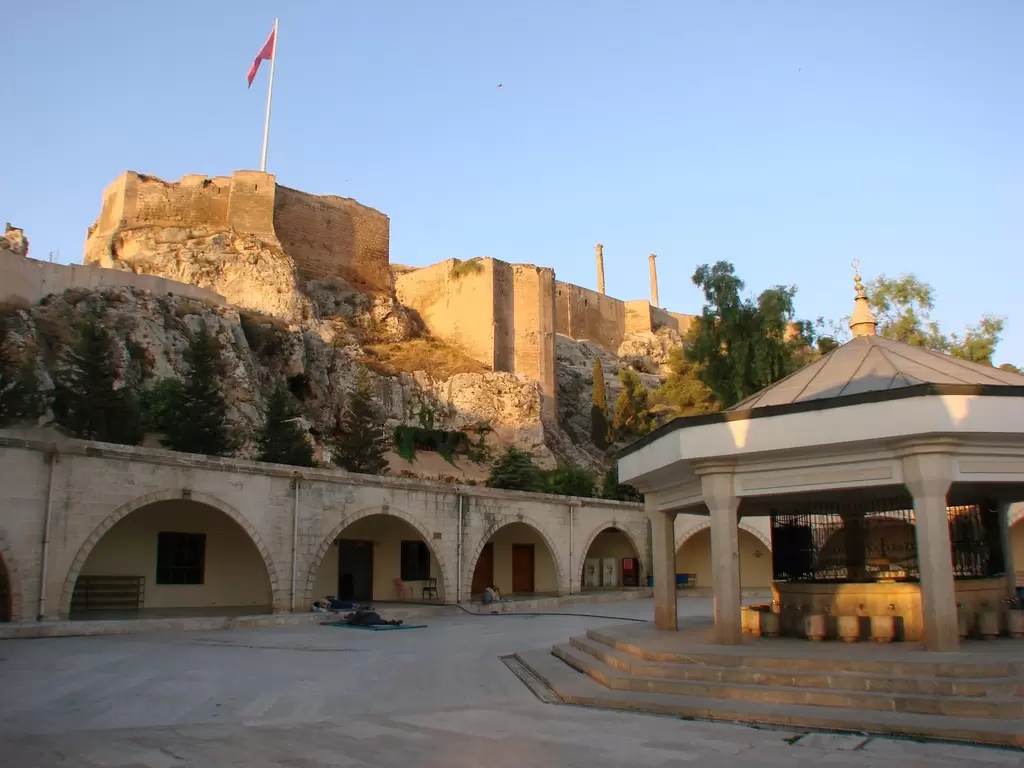
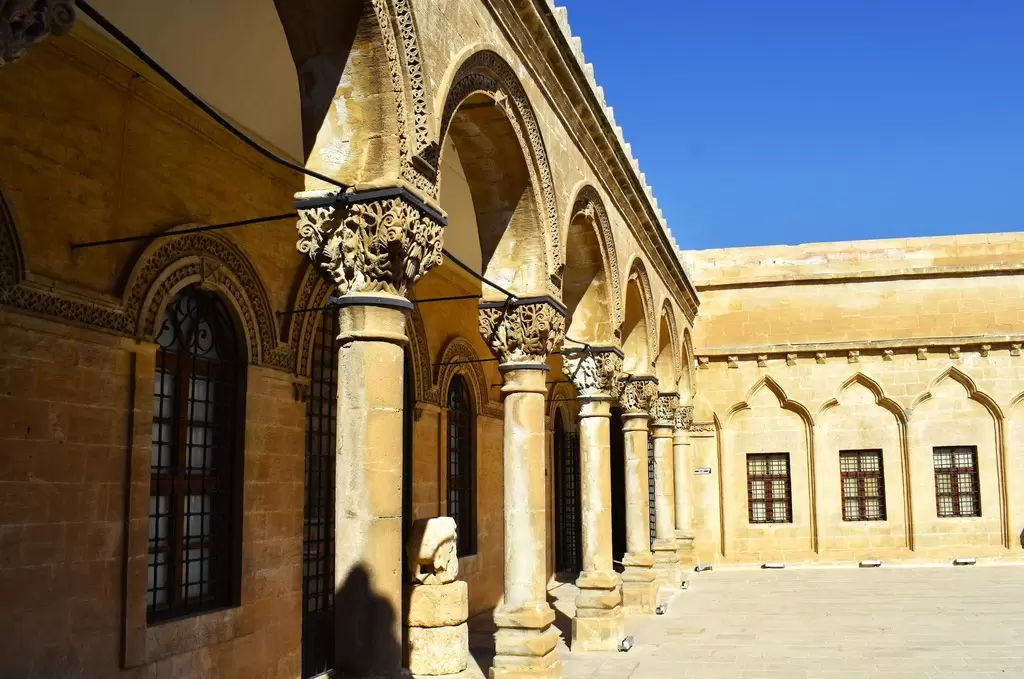
- Gaziantep: Gaziantep is famous for its rich culinary heritage. It is regarded as the gastronomic capital of Turkey, offering a wide variety of delicious local dishes and sweets. The city is also known for its well-preserved historic architecture, including the Gaziantep Castle and the Zeugma Mosaic Museum, which houses an impressive collection of Roman mosaics.
- Şanlıurfa: Şanlıurfa, often referred to as Urfa, is a city steeped in history and religious significance. It is believed to be the birthplace of Abraham and is considered a holy city by many. Şanlıurfa is home to several important religious sites, such as the Pool of Sacred Fish (Balıklıgöl) and the Cave of Abraham.
- Mardin: Mardin is renowned for its stunning architecture and unique cultural blend. The city's old town features beautiful stone houses, narrow streets, and ancient churches and mosques that showcase the region's rich historical and architectural heritage. The views from Mardin's hilltops offer breathtaking panoramas of the Mesopotamian plains.
- Batman: Batman is a rapidly growing city known for its oil industry. It is situated near the Batman River and offers opportunities for outdoor activities, such as rafting and hiking, in the surrounding natural areas.
Historical and Cultural Significance:
Southeast Anatolia is rich in historical and cultural heritage, with a history dating back thousands of years. The region has been inhabited by various civilizations, including the Assyrians, Hittites, Romans, Byzantines, and Arabs, which have left their mark on its cultural fabric. Some notable sites and attractions include:
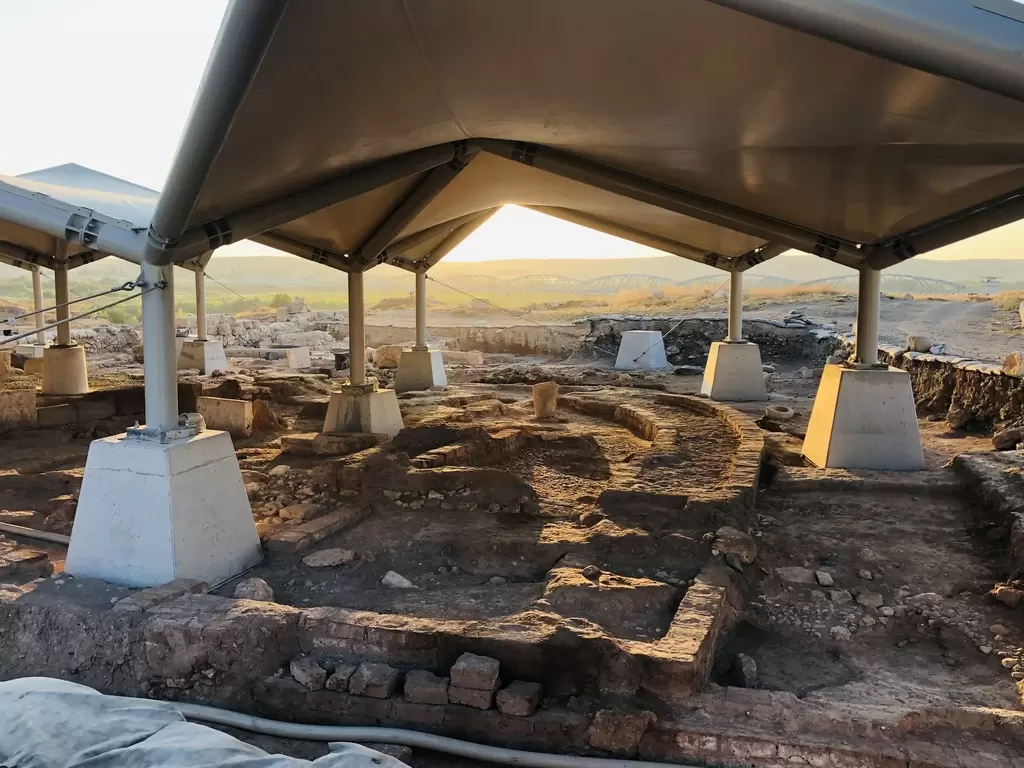
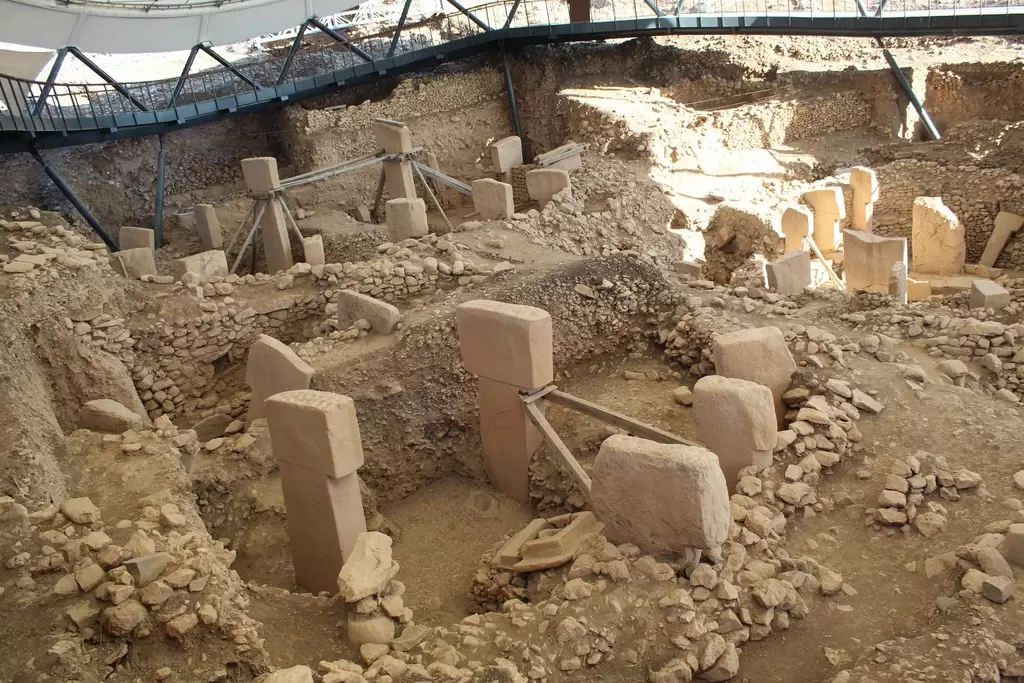
- Göbekli Tepe: Located near Şanlıurfa, Göbekli Tepe is an archaeological site that dates back to approximately 11,000 years ago. It is considered one of the oldest known human-made structures and has provided valuable insights into prehistoric societies and the development of early civilization.
- Harran: Harran is an ancient city with a history that spans over 6,000 years. It is famous for its distinctive beehive-shaped houses and the ruins of a well-preserved ancient university. The city has been a center of learning and culture throughout history.
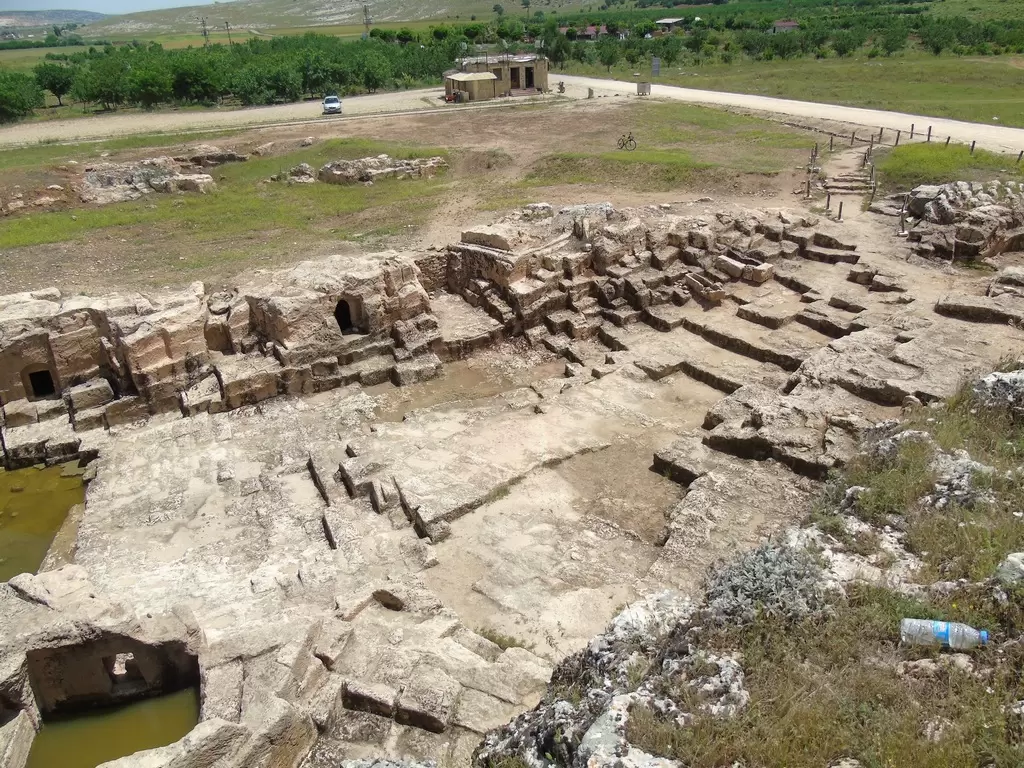
- Dara: Dara is an ancient fortress city located near Mardin. It was an important strategic stronghold during the Roman and Byzantine periods and offers visitors a glimpse into the region's military history.
- Zeugma: Zeugma, near Gaziantep, was an ancient city founded by the Seleucid Empire. It is renowned for its well-preserved Roman mosaics, which depict intricate scenes from mythology and daily life.
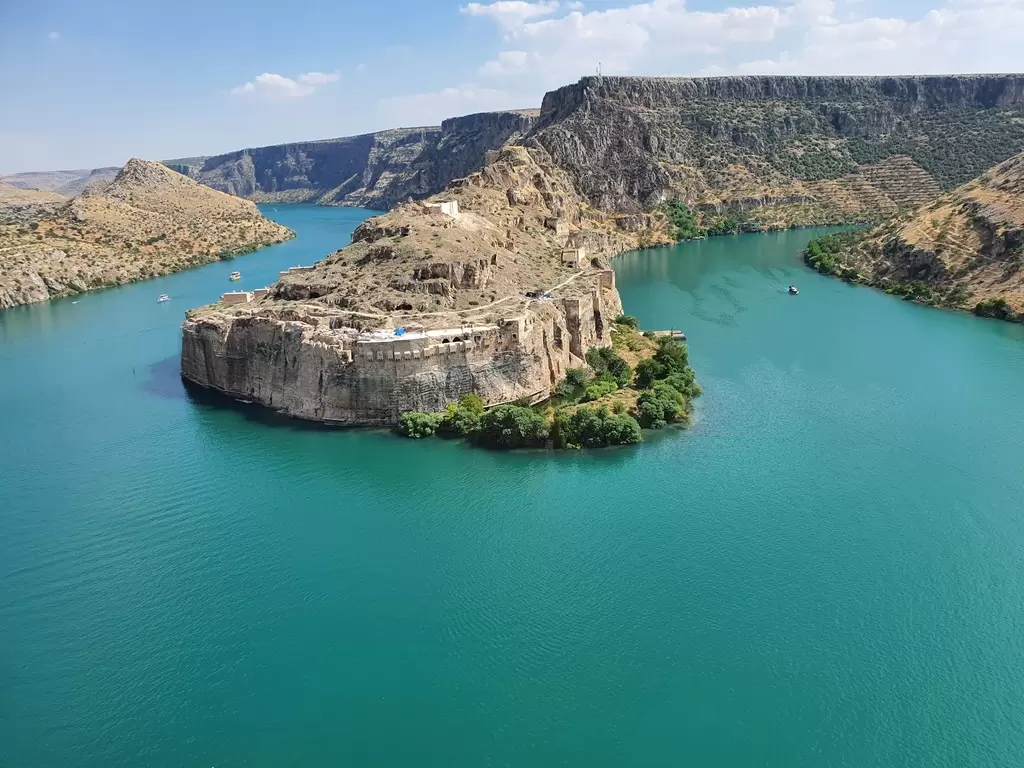
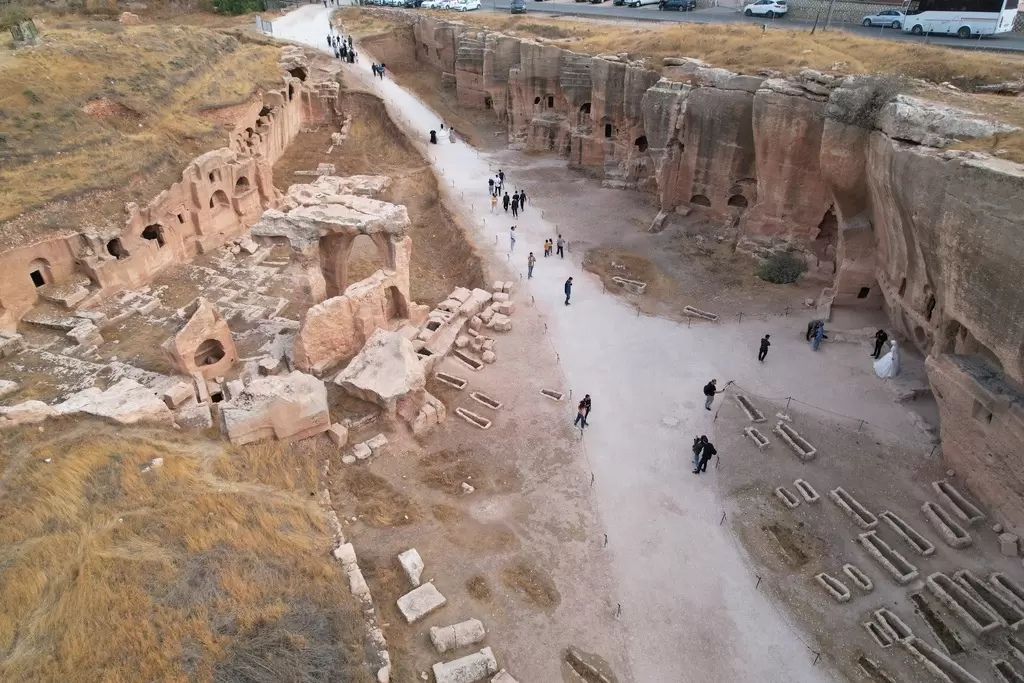
- Hasankeyf: Hasankeyf is an ancient town situated along the Tigris River. It is known for its historical significance and the presence of numerous archaeological sites, including cave dwellings, mosques, and the ruins of a medieval bridge. Due to the construction of the Ilısu Dam, Hasankeyf was relocated to a new site, preserving some of its historical structures.
Economy:
The economy of Southeast Anatolia is diverse, with agriculture, industry, and trade being major contributors. The region benefits from its fertile soil and favorable climate, making it suitable for agricultural activities such as wheat, barley, cotton, pistachio, and fruit production. The industrial sector includes textile manufacturing, food processing, automotive production, and the energy sector, with a focus on oil extraction and refining.
Natural Beauty:
Southeast Anatolia is blessed with diverse and captivating natural landscapes. The region features picturesque mountains, fertile plains, and verdant valleys. The Taurus Mountains offer opportunities for hiking, mountaineering, and winter sports. The region is also home to national parks andprotected areas, such as the Mount Nemrut National Park and the Dara Archaeological Site and Natural Park, which showcase the region's natural beauty and preserve its ecological diversity.
Transportation:
The Southeast Anatolia region is well-connected by a network of highways and domestic airports. Major cities have airports that offer domestic flights, allowing for convenient access to the region. The region's cities are also connected by rail and bus services, providing transportation options for both domestic and international travelers.
In summary, Southeast Anatolia is a region of Turkey that boasts a rich historical and cultural heritage, stunning natural landscapes, and a diverse ethnic tapestry. From the ancient sites of Göbekli Tepe and Zeugma to the vibrant cities of Diyarbakır and Gaziantep, the region offers a fascinating blend of history, culture, and natural beauty for visitors to explore and experience.


















