Kale Pepper: Detailed Information with Distinctive Features
Overview
Kale Pepper, belonging to the Capsicum annuum species in the Solanaceae family, is a distinctive agricultural product of Kale and its surrounding regions. With a history of over a century in cultivation, Kale Pepper has become a central part of local culinary traditions. Known for its versatility, this pepper is consumed in various forms, including fresh, roasted, dried, powdered, and as a base for sauces like paste or pul biber. Its vibrant flavor and adaptability to numerous dishes make it a preferred ingredient in both household and commercial kitchens.
Botanical Characteristics
The Kale Pepper plant grows to a height of approximately 50–60 cm and exhibits a robust, upright growth habit. Its broad leaves have a slightly wavy texture with prominent veins, reflecting the plant's healthy and vigorous nature. The branches exhibit normal branching, supporting the development of well-formed fruits. This pepper is characterized by its exceptional productivity, yielding fruits with a uniform shape and high-quality properties.
Fruit Characteristics
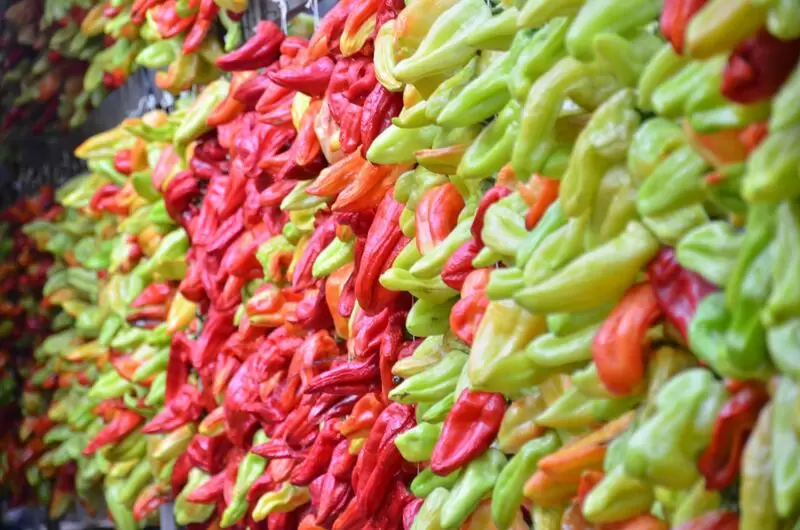
Kale Pepper fruits are typically two- or three-lobed with a slightly elongated shape. The peppers are medium-sized, with a glossy surface and a vibrant red color when fully mature. They are particularly noted for their well-balanced flavor, combining mild heat with a subtle sweetness. The flesh is thick and firm, making it ideal for a wide range of culinary uses. The peppers' porous structure and good oil content make them highly suitable for drying and grinding into powders.
Culinary Uses
Kale Pepper is a versatile ingredient with applications in both traditional and contemporary recipes. Commonly used forms include:
- Fresh Consumption: Sliced for salads or added to various dishes.
- Roasted: Used as a side dish or blended into spreads and dips.
- Dried and Ground: Processed into powdered or pul biber for seasoning.
- Paste: Incorporated into sauces or stews for enhanced flavor.
- Közleme (Roasting): Popular for its smoky aroma.
- Kurutma (Drying): Used in soups, stews, and fried dishes.
Its ability to retain flavor and texture during different processing methods makes it a favored choice in many households.
Agronomic Features
Kale Pepper is cultivated in the fertile soils of the Kale region, benefiting from the area's favorable climate. The plants are known for their healthy growth and high resilience, producing fruits with minimal defects. The peppers' thin skin and optimal moisture content make them particularly suitable for drying and storage, ensuring their availability year-round.
Cultural and Historical Significance
The cultivation of Kale Pepper dates back to at least a hundred years, reflecting its deep roots in the local culture. It is not only a staple in Kale's cuisine but also a symbol of the region's agricultural heritage. The pepper's popularity has been sustained through generations, with traditional farming techniques combined with modern advancements ensuring its continued prominence in the area.
Distinctive Features
- Bright red color and glossy appearance.
- Firm, thick flesh with a balanced sweet and spicy flavor profile.
- High oil content and porous structure, ideal for drying and grinding.
- Adaptability to diverse culinary applications.
- Sustainable cultivation practices without compromising quality.
Kale Pepper remains an irreplaceable part of the region's gastronomic identity, cherished for its rich flavor and culinary versatility.